3
Dispatch → Factbook → Miscellaneous
A Simple Solution For The Welfare State
 NIT Calculator
NIT CalculatorKeep in mind, this is a work in progress. I am open to suggestions and criticism is welcomed.
A question that runs through the people's mind: how to make government small yet effective and caring for its poorest citizens? This is one of many questions that people are constantly asking while fighting opposing ideas on how to fix the problem. So what are these ideas that people are talking about? An idea that has begun to increase in popularity is the 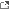 Negative Income Tax, a progressive tax system where people that make under a certain amount received a supplement instead of being taxed. Proposed by Milton Friedman, it would provide a basic income or guaranteed minimum income for its poorest citizens. It would consolidate all of the social programs within the Welfare State. It would also eliminate unnecessary programs that they were apart of. In theory it would eliminate the need for food stamps, welfare, social security, other social programs, and even the minimum wage. This would then reduce the size of government and the costs associated with it; allowing for the saved revenue to go to other programs or to the debt. Business expenses such as salaries and wages would be reduced for small businesses that hired part time; allowing them to expand and employ more people. The burden of living would be reduced for those living at or below the poverty line.
Negative Income Tax, a progressive tax system where people that make under a certain amount received a supplement instead of being taxed. Proposed by Milton Friedman, it would provide a basic income or guaranteed minimum income for its poorest citizens. It would consolidate all of the social programs within the Welfare State. It would also eliminate unnecessary programs that they were apart of. In theory it would eliminate the need for food stamps, welfare, social security, other social programs, and even the minimum wage. This would then reduce the size of government and the costs associated with it; allowing for the saved revenue to go to other programs or to the debt. Business expenses such as salaries and wages would be reduced for small businesses that hired part time; allowing them to expand and employ more people. The burden of living would be reduced for those living at or below the poverty line.
Of course, a Negative Income Tax is not enough to fix and reform the Welfare State. It must harmonized with several other ideas to work perfectly in the 21st century. One of those ideas is another tax: 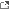 Land Value Tax, a tax on unimproved value of land. Also a progressive tax like the NIT, it's like the property tax but it disregards the value of buildings, personal property and other improvements on said land. It has been advocated by economists such as Adam Smith, David Ricardo, Henry George, and even Milton Friedman because it is straightforward: you only need the valuation of the land a title register. While this tax can't replace all of the taxes, it would be more difficult to avoid to pay unlike some of the other taxes currently in place. This tax has been implemented in several countries and has worked nicely. This would help gain additional revenues to help fund the government and encourage businesses to use the land and grow the economy.
Land Value Tax, a tax on unimproved value of land. Also a progressive tax like the NIT, it's like the property tax but it disregards the value of buildings, personal property and other improvements on said land. It has been advocated by economists such as Adam Smith, David Ricardo, Henry George, and even Milton Friedman because it is straightforward: you only need the valuation of the land a title register. While this tax can't replace all of the taxes, it would be more difficult to avoid to pay unlike some of the other taxes currently in place. This tax has been implemented in several countries and has worked nicely. This would help gain additional revenues to help fund the government and encourage businesses to use the land and grow the economy.
A third thing that must go along with this is a Tax Credit and Tax Expenditure system. A 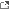 Tax Credit is a tax incentive that reduces the tax bill directly as a
Tax Credit is a tax incentive that reduces the tax bill directly as a  Tax Expenditure is basically government spending through the tax code. By combining these two ideas, this would help poor to middle class individuals and families to either write off certain expenses or reduce the cost of purchasing certain goods and services like Healthcare, education, gas, etc. This would reduce the burden on the lower and middle class while reducing the need for government interference in important sectors of the economy and controlling them as such. Of course, there can't be a Tax Credit or Tax Expenditure for everything but by taking caring the essentials, it would reduce government interference and allow them to focus on other important programs on the federal level.
Tax Expenditure is basically government spending through the tax code. By combining these two ideas, this would help poor to middle class individuals and families to either write off certain expenses or reduce the cost of purchasing certain goods and services like Healthcare, education, gas, etc. This would reduce the burden on the lower and middle class while reducing the need for government interference in important sectors of the economy and controlling them as such. Of course, there can't be a Tax Credit or Tax Expenditure for everything but by taking caring the essentials, it would reduce government interference and allow them to focus on other important programs on the federal level.
A fourth and final thing that must be done is to simple taxes for individuals/families and businesses. Currently, the tax code is complicated for businesses and individuals/families. This is because of the rules and regulations within the tax code such as the Tax Credits, Tax Expenditures, and what deductions can be used. But you are wondering: why advocate for Tax Credits and Tax Expenditures when then complicate things? The reason is that there are too many requirements to qualify for these things and has in affect disqualified some from getting the help needed to support their family. Then there is the business part of the tax code where many take advantage of the loopholes within it. The Tax Code tries to squeeze as much out as possible but fails to do so fully and does it in a negative effect. There is also the fact many small businesses struggle with the tax code as it's complicated and that it burdens them rather than encourages them. Simplifying the Tax Code will prompt small businesses to stay in business, gather the necessary revenue from large corporations without driving them overseas, and give individuals and families in the lower income bracket to improve their lives and reduce the burden of living.
A combination of all these programs and ideas would allow for economic growth; businesses will be able to hire people and cut costs. At the same time, we will be able to help those that struggle by and help them get back on their feet. There will need to be more things done to get to fixing any problems a nation faces such as responsible spending and common sense regulations but this is where we can start. Yet, many continue to believe in the many of the same old ideas while disregarding ideas that are plausible and can actually make a difference. With so many ideas to the mix, I think we can offer some new thoughts that can innovate a nation. Since you know what everything means up here, let's get to the proposal shall we? So here's my proposal I would lay out.
What Would Change?
The Alternative Minimum Tax, Estate Tax, Death Tax, and Payroll Tax would be eliminated though most should be gradually eliminated overtime. It would lower the Capital Gains Tax gradually over a period of 5 years.
Individuals
Negative Income Tax for individuals and families will be adopted.
For individuals that make $15,000 or less, will be taxed exempt. The subsidy rates (SR) will be set as follow: 0-50%
A person earning $0-2,499 would have a subsidy rate of 50%.
A person earning $2,500-4,999 would have a subsidy rate of 40%.
A person earning $5,000-7,499 would have a subsidy rate of 30%.
A person earning $7,500-9,999 would have a subsidy rate of 20%.
A person earning $10,000-12,499 would have a subsidy rate of 10%.
A person earning $12,500-15,000 would have a subsidy rate of 5%*.
Example: You earned $5,000 for the year. The NIT is set at $15,000.
Tax returned: (15,000-5,000)*(30%)= $3,000 is given.
*Those that are within $500 or less of $15,000 would not receive a subsidy rate but are still taxed exempt. Those above $500 will have a 5% subsidy rate applied.
For individuals that make $15,000 or above, they will be taxed. The tax rates (TR) will be set as followed: 0-35%
A person earning $15,000-39,999 would have a tax rate of 10%*.
A person earning $40,000-99,999 would have a tax rate of 15%.
A person earning $100,000-174,999 would have a tax rate of 20%.
A person earning $175,000-499,999 would have a tax rate of 25%.
A person earning $500,000-999,999 would have a tax rate of 30%.
A person earning $1,000,000+ would have a tax rate of 35%.
Example: You earned $25,000 for the year. The NIT is set at $15,000.
Tax paid: (25,000-15,000)*(10%)= $1,000 is the amount paid in taxes.
*For those that are over $500 or less of $15,000, will be taxed exempt. Above $500 has a tax rate of 10%.
Married/Joint
Those that are married/joint and make $30,000 or less, will receive a tax subsidy. The subsidy rates will be as follow: 0-50% times 1.5 of the amount received will be the final amount collected.
A Family earning $0-4,999 would have a subsidy rate of 50%x1.5.
A Family earning $5,000-9,999 would have a subsidy rate of 40%x1.5.
A Family earning $10,000-14,999 would have a subsidy rate of 30%x1.5.
A Family earning $15,000-19,999 would have a subsidy rate of 20%x1.5.
A Family earning $20,000-24,999 would have a subsidy rate of 10%x1.5.
A Family earning $25,000-30,000 would have a subsidy rate of 0-5%*x1.5.
Example: The married/joint couple earned $5,000 for the year. The NIT is set at $30,000.
Tax returned: (30,000-5,000)*(40%)*(1.5)= $15,000 is given.
*Those that are within $1,000 or less of $30,000 would not receive a subsidy rate but are still taxed exempt. Those above $1,000 will have a 5% subsidy rate applied.
For those that are married/joint that make $30,000 or above will be taxed. The tax rates (TR) will be set as followed: 0-35%
A person earning $30,000-74,999 would have a tax rate of 10%*.
A person earning $75,000-99,999 would have a tax rate of 15%.
A person earning $100,000-274,999 would have a tax rate of 20%.
A person earning $275,000-499,999 would have a tax rate of 25%.
A person earning $500,000-999,999 would have a tax rate of 30%.
A person earning $1,000,000+ would have a tax rate of 35%.
Example: The married/joint couple earned $50,000 for the year. The NIT is set at $30,000.
Tax paid: (50,000-30,000)*(10%)= $2,000 is the amount paid in taxes.
*For those that are over $1,000 or less of $30,000, will be taxed exempt. Above $1,000 has a tax rate of 5%.
Retirement/Disabled
For those that are retiring or are disabled, $30,000 dollars will be tax exempt. Depending at the age of retirement will depend on the subsidy rate of return. Also, public workers that collect a pension within their own State will follow the $30,000 dollars that is exempted. Disable, three age groups, and pension scenario are considered as follow:
Those that are disabled will have a subsidy rate of 50%.
Those retiring between the Ages 68-69 will have a subsidy rate of 50%.
Those retiring between the Ages 69-70 will have a subsidy rate of 55%.
Those retiring between the Ages 70+ will have subsidy rate of 60%.
Pension Case- Subsidy:
A person earning $0-9,999 would have a subsidy rate of 50%.
A person earning $10,000-19,999 would have a subsidy rate of 25%.
A person earning $20,000-30,000 would have a subsidy rate of 10%*.
*Those that are within $1,000 or less of $30,000 would not receive a subsidy rate but are still taxed exempt. Those above $1,000 will have a 5% subsidy rate applied.
Pension Case- Tax:
For those earning $35,000+ would have a tax rate of 5%.
Unemployment Benefits
Those that were laid off can get unemployment benefits depending on how much they were paid:
~Those that make under $15,000 would be able to qualify for $250 a week (total of $13,000 a year).
~Those that make $15,000-29,999 would be able to qualify for $375 a week (total of $19,500).
~Those that make $30,000+ would qualify for $500 a week (total of $26,000 a year).
This would then follow the individual NIT subsidy rate of 50% after 1-2 years.
Individual/Family Expenditures
Along with the NIT and Tax Credits (see below), tax expenditures (credits) should be provided to those below the NIT or above the NIT depending on the circumstances. Here are the following kinds of expenditures people could qualify for:
Food Expenditure- Similar to food stamps, it would allow low income individuals/families to purchase only food with such credits. Unlike food stamps though, it would be a percentage of the NIT they received from the government. Individuals that make above $14,500 or families above $29,000 would not qualify for this expenditure:
Individual Food Expenditure
Those that receive a 50% subsidy rate will get a Food Expenditure of $100 a month.
Those that receive a 40% subsidy rate will get a Food Expenditure of $75 a month.
Those that receive a 30% subsidy rate will get a Food Expenditure of $50 a month.
Those that receive a 20% subsidy rate will get a Food Expenditure of $25 a month.
Those that receive a 5-10% subsidy rate will get a Food Expenditure of $10 a month.
Example: The individual received $7,500 from the NIT. The Food Expenditure is $100 a month. Food Expenditure received: $1,200 (100x12).
Family Food Expenditure
Those that receive a 50% subsidy rate will get a Food Expenditure of $200 a month.
Those that receive a 40% subsidy rate will get a Food Expenditure of $150 a month.
Those that receive a 30% subsidy rate will get a Food Expenditure of $100 a month.
Those that receive a 20% subsidy rate will get a Food Expenditure of $50 a month.
Those that receive a 5-10% subsidy rate will get a Food Expenditure of $25 a month.
Example: The family received $11,250 from the NIT. The Food Expenditure is $200 a month. Food Expenditure received: $2,400 (200x12).
Medical Expenditure- This kind of expenditure would be given to individuals and families to help reduce the cost of healthcare. The purpose of this credit is to help the individual/family purchase private health insurance. It is also to help reduce the bill of said insurance. Those that either take advantage of the Healthcare Credit (see below) or individuals that make above $50,000 or families that make above $75,000 would not qualify for this expenditure:
Individual Medical Expenditure
Those that receive a 5-50% subsidy rate will get a Medical Expenditure of $4,000 a year.
Those that make between $15,000-39,999 will get a Medical Expenditure of $2,000 a year.
Those that make between $40,000-50,000 will get a medical Expenditure of $1,000 a year.
Family Medical Expenditure
Those that receive a 5-50% subsidy rate will get a Medical Expenditure of $6,000 a month.
Those that make between $30,000-74,999 will get a Medical Expenditure of $2,000.
Individual/Family Tax Credits
Lower and middle class individuals/families can qualify for one of several tax credits:
Healthcare Credit- Anyone can reduce their taxable income by taking up to $10,000 of the health insurance they paid for. Those making above $110,000 or opt to take advantage of the Medical Expenditure will not qualify for the credit.
Education Credit- Anyone can reduce their taxable income by taking 10-25% of the education paid to a private school or college/university. For individuals that make $60,000+ or families making $75,000+ will not be able to qualify for the credit.
Individual
Those making under $25,000 will be allow to take 25% of their college tuition they paid for.
Those that make $25,000-29,999 will be allow to take 15% of their college tuition they paid for. Those that make $30,000-59,999 will be allow to take 10% of their college tuition they paid for.
Family
Those making under $30,000 will be allow to take 25% of their college tuition they paid for.
Those that make $30,000-74,999 will be allow to take 15% of their college tuition they paid for.
Commodity Credit- Anyone can reduce their taxable income by taking 10% of the utilities they paid. They can also take their property taxes they paid for on a State and Local level. This will end when an individual/family makes $65,000+ unless it is their property taxes which they can take the full amount.
Child Credit- Individuals/Families will be allow to reduce their taxable income by $0-1,000 per a child. Those making $200,000+ will not qualify for the credit.
Those making under $125,000 will get $1,000 per child.
Those making $125,000-149,999 will get $500 per child.
Those making $150,000-199,999 will get $250 per child.
Housing Credit- This can be used when a household pays their mortgage. Anyone can reduce their taxable income by taking either 10% or $2,500 off of the mortgage/rent they paid. Those making $250,000+ will not qualify for the credit.
Green Credit- This can be used when a household installs green energy saving products. Anyone can reduce their taxable income by taking 10% of the installation cost.
Businesses
Corporate taxes need to be reformed to taxed more effectively by eliminating the loopholes and reduce corporate inversion. This should be settled by taxing within a nation's borders (territorial basis) rather then attempting to globally tax (global basis) them. However, businesses must also be protected from foreign takeovers. To do this, the tax code for businesses needs to be simplified (including sole proprietorships). A new Corporate Tax will be formed and shall be as follow:
A business that earns between $0 to 14,999 will pay 0%.
A business that earns between $15,000 to 99,999 will pay 5% + $1,000.
A business that earns between $100,000 to 449,999 will pay 10% + $2,500.
A business that earns between $500,000 to 2,499,999 will pay 15% + $10,000.
A business that earns between $2,500,000 to 7,999,999 will pay 20% + $25,000.
A business that earns between $8,000,000+ will pay 25% + $100,000.
Example: The business has a profit of 100,000. The tax bracket is 10% + $2,500.
Tax paid: (100,000*10%)+ 2,500= $12,500 is the amount paid in taxes.
Dividends
When dividends are issued, this additional income will be considered as ordinary income to the shareholder. The income earned from the dividend(s) would follow the NIT tax brackets for individuals or married/joint. In the case of sole proprietorship, the sole owner's income will be taxed on the basis of the NIT as well.
For Individuals:
Example 1: You earned $10,000 from a dividend received. The NIT is set at $15,000.
Tax paid: (15,000-10,000)*(10%)= $500 is the amount given.
Example 2: You earned $25,000 from a dividend received plus a $35,000 salary earned. The NIT is set at $15,000.
Tax paid: (25,000+35,000-15,000)*(10%)= $4,500 is the amount paid in taxes.
For Married/Joint:
Example 1: You earned $10,000 from a dividend received plus a $10,000 salary earned from your spouse. The NIT is set at $30,000.
Tax paid: (30,000-20,000)*(10%)*(1.5)= $1,500 is the amount given.
Example 2: You earned $25,000 from a dividend received plus a $35,000 salary earned from your spouse. The NIT is set at $30,000.
Tax paid: (25,000+35,000-30,000)*(10%)= $3,000 is the amount paid in taxes.
Business Tax Credits
Businesses will be able to qualify for certain tax credits as follow:
Health Insurance Credit- Any business can reduce their taxable income if they provide healthcare for their employees. Businesses can reduce their taxable income by the amount of healthcare given for each employee.
Paid Leave Credit- This can be used when a business offers paid leave for their employees when said employee is sick, has an emergency, or birth of a child. Businesses can reduce their taxable income by up to $3,500 per employee and offer between 4-10 weeks of paid-leave.
Commodity Credit- Any business can reduce their taxable income by taking 10% of the utilities they paid. They can also take their property taxes they paid on a State and Local level as a reduction as well. Businesses making $1,000,000+ will not qualify for the credit except in the case of property taxes, which they can take the full amount.
Education Credit- Any business can reduce their taxable income if they provide to cover the cost of education for their employees. Businesses can reduce their taxable income by the amount paid towards the employee's education.
Business Credit- This can be used when a business has paid rent or a mortgage on the business. Businesses can reduce their taxable income by 15%. Businesses making $1,000,000+ will not qualify for the credit.
Green Credit- This can be used when a business installs green energy saving products. Any business can reduce their taxable income by taking 10% of the installation cost.
Capital Gains Tax
To ensure that the government is funded and to reduce income inequality, a Capital Gains Tax (CGT) would still be in place. However, this tax will be lowered over a five year period and simplified to ensure and encourage innovation and investments while at the same time reducing the burden on lower to middle income families. Total gains and losses will be subtracted to determine whether the individual/family or business has a gain or a lost at the end of the year once it is realized. The following will be covered under this section: short term capital gains/losses and long term capital gains/losses.
Short Term Capital Gains/Losses
Originally taxed at ordinary income rates, this will now be changed to follow the negative income tax rates. The full amount will be taxed based on the CTG Rate.
Individuals/Families:
A person/family in the 10-15% bracket will Capital Gains Tax Rate of 0%.
A person/family in the 20% bracket will Capital Gains Tax Rate of 5%.
A person/family in the 25% bracket will Capital Gains Tax Rate of 10%.
A person/family in the 30% bracket will Capital Gains Tax Rate of 15%.
A person/family in the 35% bracket will Capital Gains Tax Rate of 20%.
Example 1: You have a short term capital gain of $2,000 for the year. You are in the 25% bracket for the NIT.
Tax paid: $2,000*10%= $200 is the amount paid in taxes.
In the event that a loss is realized when total gains and losses are subtracted, then only losses within the year that occur may be carried over at 20% for each year on the individual/family's taxes until the total lost is recaptured. Those in the 10-15% tax brackets will be allow to take the full lost of their taxes.
Example 1: You have a short term capital loss of $2,000 for the year. You are in the 25% bracket for the NIT.
Amount that can be deducted: $2,000*20%= $400.
Businesses:
A business in the 5-10% tax bracket will have a Capital Gains Tax Rate of 0%.
A business in the 15% tax bracket will have a Capital Gains Tax Rate of 10%.
A business in the 20% tax bracket will have a Capital Gains Tax Rate of 12.5%.
A business in the 25% tax bracket will have a Capital Gains Tax Rate of 15%.
Example 1: You have a short term capital gain of $2,000 for the year. You are in the 25% bracket for the NIT.
Tax paid: $2,000*15%= $300 is the amount paid in taxes.
In the event that a loss is realized when total gains and losses are subtracted, then only losses within the year that occur may be carried over at 25% for each year for the business until the total lost is recaptured. Those in the 5-10% tax brackets will be allow to take the full lost off their taxes.
Example 1: You have a short term capital loss of $2,000 for the year. You are in the 25% bracket for the NIT.
Amount that can be deducted: $2,000*25%= $500.
Long Term Capital Gains/Losses
This will also follow the negative income tax rates. The full amount will be taxed based on the CTG Rate.
Individuals/Families:
A person/family in the 10-15% bracket will Capital Gains Tax Rate of 0%.
A person/family in the 20-25% bracket will Capital Gains Tax Rate of 10%.
A person/family in the 30-35% bracket will Capital Gains Tax Rate of 15%.
Example 1: You have a long term capital gain of $5,000 for the year. You are in the 25% bracket for the NIT.
Tax paid: $5,000*10%= $500 is the amount paid in taxes.
In the event that a loss is realized when total gains and losses are subtracted, then only up to $3,000 of that could be carried forward for five years.
Example 1: You have a long term capital loss of $5,000 for the year. You are in the 25% bracket for the NIT.
Amount that can be deducted: $5,000-$3,000= $2,000.
Businesses:
A business in the 5-10% tax bracket will have a Capital Gains Tax Rate of 0%.
A business in the 15-20% tax bracket will have a Capital Gains Tax Rate of 10%.
A business in the 25% tax bracket will have a Capital Gains Tax Rate of 15%.
Example 1: You have a long term capital gain of $5,000 for the year. You are in the 25% bracket for the NIT.
Tax paid: $5,000*15%= $750 is the amount paid in taxes.
In the event that a loss is realized when total gains and losses are subtracted, then only up to $5,000 of that loss can carried forward for five years or back three years.
Example 1: You have a long term capital loss of $5,000 for the year. You are in the 25% bracket for the NIT.
Amount that can be deducted: $5,000-$5,000= $0
Land Value Tax  Valuation Idea
Valuation Idea
(NOTE- It was difficult to find numbers for valuing property. If you have numbers, please send them to me so I can adjust.)
Along with a NIT and Corporate Taxes, comes a Land Value Tax. Since it is a tax on unimproved land, buildings, personal property, and improvements. are excluded from the LVT. Only the unimproved land is taxed. Land valuations will be based on market valuations and capital values. There will be two rates as follow:
Land that is valued under $20,000 will not be taxed.
Land that is valued $20,000-99,999 will be subjected to a 2.5% LVT.
Land that is valued $100,000+ will be subjected to a 5% LVT.
Narcotic Tax
A Narcotic Tax would be in place for drugs such as Cocaine, Marijuana, Heroine, etc. It would not include non-prescription and prescription drugs. The tax will be included in the final price and shown to the consumer before purchasing any drug*. The rates are capped and are as follow:
Marijuana: 1%.
Other drugs: 5%.
*For instance, if 1 oz. of Marijuana is $3, a 1% tax is applied. The total cost for that 1 oz. of marijuana is $3.03. The tax is already calculated into the price and is shown to the consumer before they purchase it.
Medical Savings Tax
To ensure and help some that can't pay for medical expenses, a federal medical savings account system will be developed. Similar to the successful program known as  Medisave, this program would helped the average American with medical bills and establish Medical Savings Accounts (MSA). Each account is for each individual. It would only be strictly for medical purposes. These accounts will also not be taxed whether it remains in the account or is withdrawn. This account though will be optional to set up and must be decided by the individual to open and set up the account when they go for their first job/turn 18 years of age/sign up. If an account is set up, the rate is as follow:
Medisave, this program would helped the average American with medical bills and establish Medical Savings Accounts (MSA). Each account is for each individual. It would only be strictly for medical purposes. These accounts will also not be taxed whether it remains in the account or is withdrawn. This account though will be optional to set up and must be decided by the individual to open and set up the account when they go for their first job/turn 18 years of age/sign up. If an account is set up, the rate is as follow:
A rate of 5% on wages/salaries per paycheck*
*Those that earn a subsidy from the government based on the individual NIT Brackets will be taxed the same as well.
Businesses will be required to match 2% of that employee's wage/salary to his/her MSA. Businesses are exempt from paying this tax if they make less than $2,500,000 or provide healthcare to their employees.
Other Rules/Mentions
There are of course other rules such as accounting procedures and what can be deducted. Passive income, other kinds of dividends, capital gains/loses, etc. all have an effect on the tax code as well. I may not be able to mention everything so I would do my best of course. If you want me to add/change/remove anything, let me know.
